Contents
Resource 7: Decision Analysis¶
Select A Decision Framework¶
It is helpful to consider how decisions will be made for material selection early on in the evaluation process. A decision method can drive information needs and the criteria to be applied moving forward.
Some decision-making approaches are simpler than others to apply, use fewer resources and therefore cost less to implement. Currently, there are three decision methodologies used in the alternatives assessment (AA) process, i.e. the Sequential, Simultaneous and Hybrid Methodologies. In general, the Sequential Method provides the greatest cost savings because it can help narrow down options early in the assessment process.
The Simultaneous Method is the most expensive to implement and has the greatest data needs. It requires comparison of results for all of the available options and for all considerations and criteria.
Transparency is Key¶
Wherever there are tradeoffs, transparency can support credibility and ensure that decisions are clear and understandable. Decision support tools that are ‘black boxes’ or that provide results without transparency are not recommended because it will not be clear if the assessment aligns with the stated goals and objectives of the product designer.
Sequential Framework¶
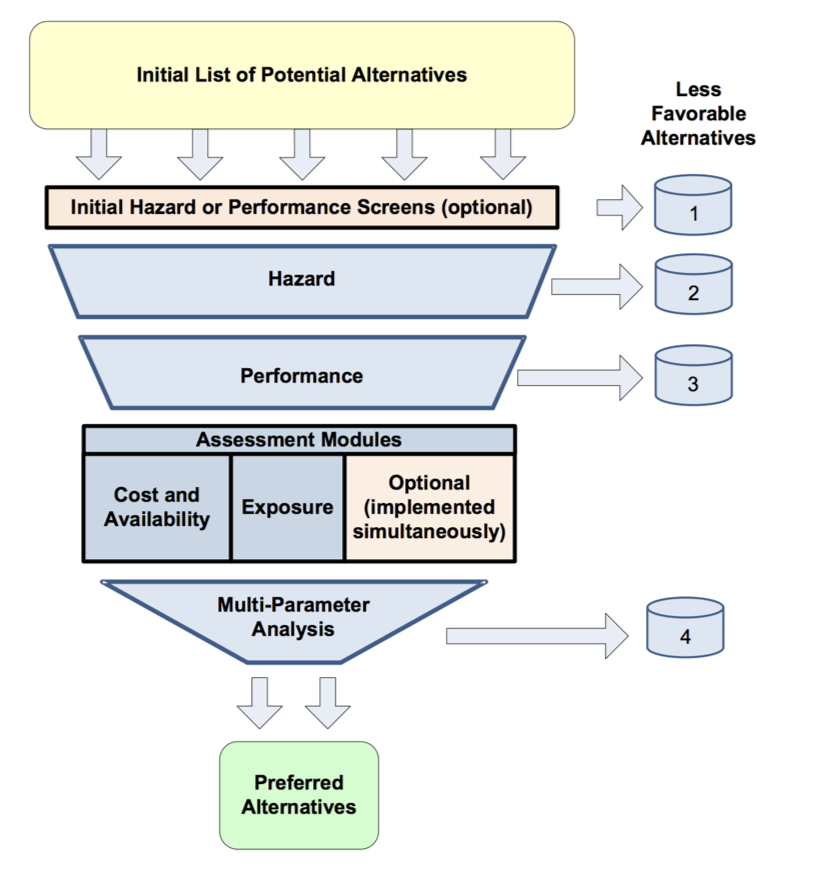
In the Sequential approach, decisions are made at each evaluation point and only those alternatives that meet or exceed the criteria at any point continue on for further evaluation.
The best analogy is a sieve where at each point along the process, the data collected are used to differentiate between acceptable alternatives and those that do not have desired characteristics. At each point, data are collected only on those alternatives that pass through the prior sieve and the reasons for eliminating plastic options are documented.
Documentation along the way is important. It both enables others to understand the process but also could be needed if at the end of the assessment no viable alternatives are identified. The product developer may choose to revisit and alter decisions along the way in order to identify a viable option.
The benefits of the Sequential approach is that it is cost effective. Data gathering is costly with respect to time, expertise and money. At each step in the Sequential approach, the number of viable alternatives decreases, restricting data collection needs to only those that meet or exceed criteria and eliminating the need for further data collection on alternatives that have been screened out. The Sequential approach also has the benefit of facilitating a final recommendation more quickly than the other decision methodologies. For these reasons, it is a commonly used technique in the alternatives assessment process.
One negative aspect of the Sequential Methodology has limited its use by some organizations. At the end of the process, the alternatives identified may not include the optimal alternative(s) when one considers all the data simultaneously. As with most decisions, there are often tradeoffs between criteria. In the Sequential approach, an alternative may be eliminated early on based on one category, but it may be a preferred alternative based on the full set of criteria.
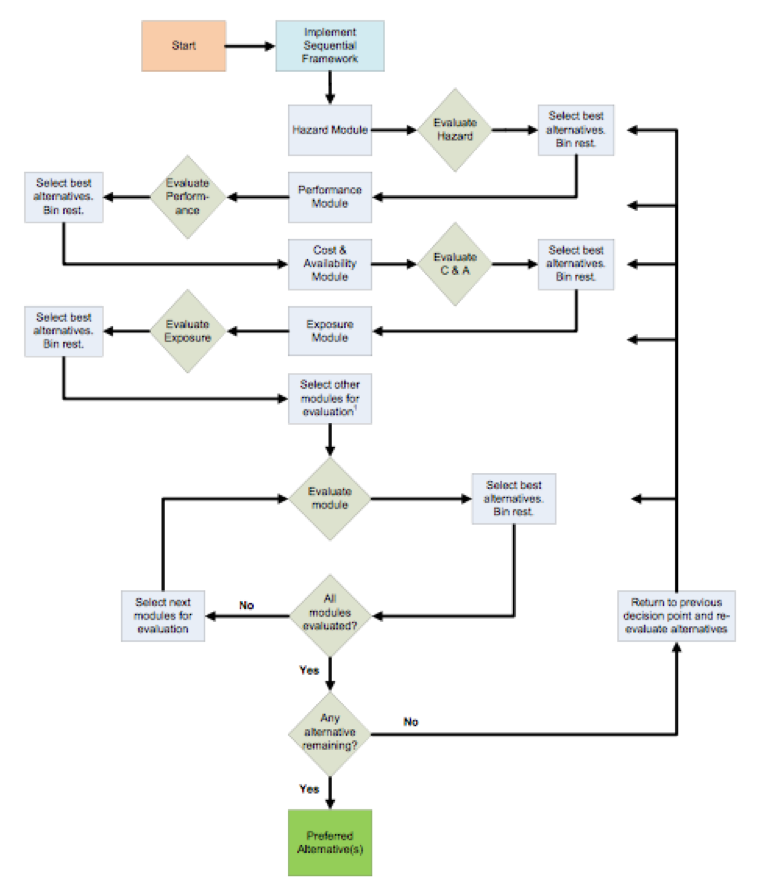
image
Using the parameters of Hazard, Performance, Cost & Availability and Exposure, the above flow chart illustrates how the Sequential approach to decision support would help to identify preferred alternatives.
Simultaneous Framework¶
In the Simultaneous approach, data are collected on all alternatives for all relevant categories and criteria. The product developer then creates a framework and a weighting scheme and documents the decision criteria. Using the data collected, all of the alternatives are compared against the desired criteria simultaneously. When more than one material is found to be viable, additional criteria may be applied to further refine the preferred alternatives.
The benefit of the Simultaneous approach is that it retains more options throughout the decision-making process. The Simultaneous approach identifies materials with the lowest overall impact to human health and the environment. However, while optimized for an overall score, a material may be sub-optimal for any one category.
The negative side of the Simultaneous approach is that it is expensive and labor intensive because data are collected on all possible alternatives. In addition, the product developer must create ranking criteria against which all the alternatives are compared. Data gaps may become more of an issue because more data are needed. For these reasons, some organizations opt not to use the Simultaneous approach.
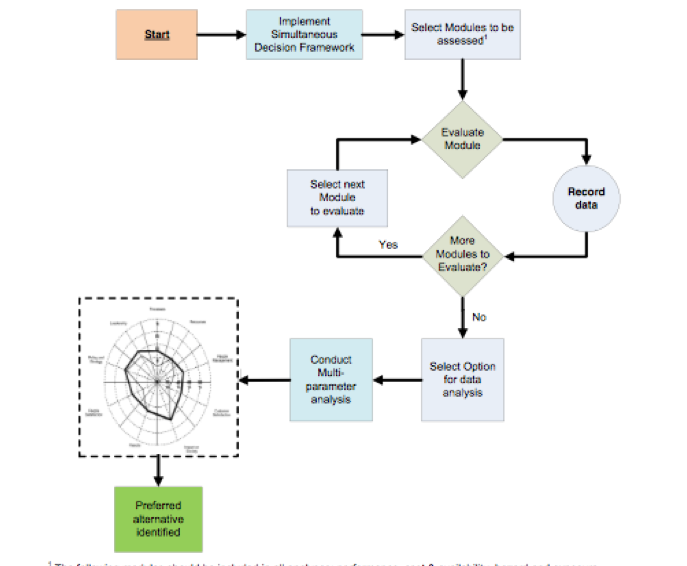
image
Using the parameters of Hazard, Performance, Cost & Availability and Exposure, the above flow chart illustrates how the Simultaneous approach to decision support would help to identify preferred alternatives.
Hybrid Framework¶
The Hybrid approach, as its name indicates, is a mixture of the Sequential and Simultaneous approaches. In the Hybrid approach, the Sequential approach is used for a few criteria and the alternatives that remain at the end of that process are subjected to further evaluation using the Simultaneous approach. For example, an organization may decide to use the Sequential approach for the performance and toxicity evaluations. Only those chemicals or materials that meet or exceed the performance requirements are submitted for a toxicity evaluation. Upon completion of the toxicity evaluation, only those chemicals or materials that meet or exceed toxicity requirements are evaluated using the Simultaneous approach for the remaining decision criteria.
The Hybrid approach has the benefit of addressing to a degree the pros and cons identified for the Sequential and Simultaneous approaches. By using the Sequential approach, cost and resource requirements are reduced by concentrating limited resources on the most viable candidates. By using the Simultaneous approach, evaluation is conducted on a broader pool of alternatives.
Because of its flexibility and its optimized use of resources, the Hybrid approach may be the preferred approach for evaluating alternatives.
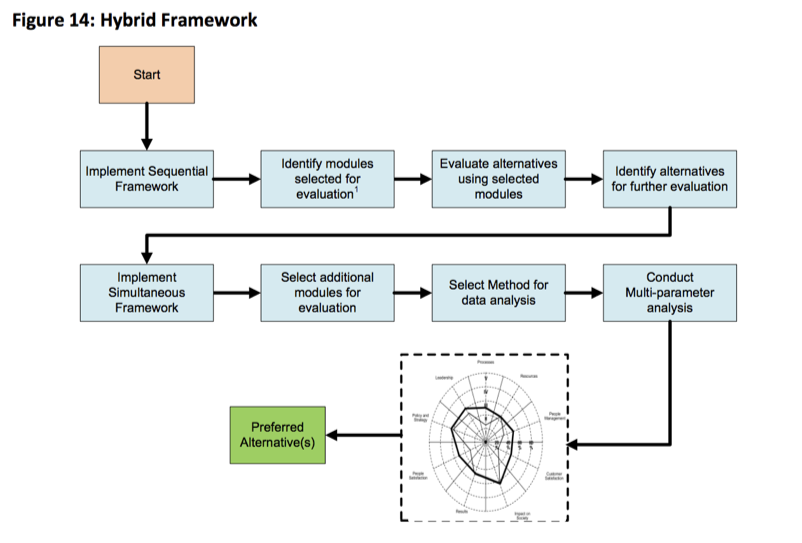
image
The Hybrid Framework combines elements of the Sequential approach and the Simultaneous approach. First the Sequential approach is used to rule out those options that fail the initial screening criteria. Then the Simultaneous approach is used to compare all of the remaining options for all of the remaining criteria at the same time.